¶ Search IOCs
This section is designed to help you search for indicators such as IP addresses, domains, and URLs, and even validate SMS messages containing links to check if they are legitimate. You can search across multiple open-source threat intelligence feeds and benefit from AI-powered insights that enhance the accuracy of the information gathered.
We are constantly working on bringing more trusted feeds that are widely used by the security community.
Special thanks to all the open-source threat intelligence feed providers for their invaluable support to the community. If you feel any feed is missing and it’s open-source, feel free to submit a feature request in our contact form.
¶ IOC Search & Lookup
The IOC Search module allows users to perform powerful lookups on Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) such as IP addresses, URLs, and Domains. It aggregates data from multiple vendors and internal sources, providing a centralized view of intelligence and context.
¶ Features Overview
- Cross-vendor Lookup: Checks IOCs against multiple vendor feeds (blacklists & whitelists).
- Reputation Score: Aggregated threat score from:
- VirusTotal
- AbuseIPDB
- AlienVault OTX - Internal Scoring Logic
- Network, Host, WhoIs, Certificate, Behaviour Info
- Search Timeline: Shows how frequently the IOC has been searched in the last 30, 60 or 90 days.
- Bulk Lookup: Supports batch analysis of up to 20 indicators at once.
¶ Categories
Malwareis harmful software designed to damage or exploit systems, networks, or devices. We categorize any IP, domain, or URL involved in malware-related activities under the "Malware" category.Phishinginvolves deceptive practices where attackers try to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or personal details, by pretending to be trustworthy entities. Any IP, domain, or URL involved in phishing activities is categorized under the "Phishing" category.Botnetconsist of networks of compromised computers that are controlled remotely to perform malicious activities, often without the users' knowledge. IPs involved in scanning or exhibiting bot-like behaviors are categorized under the "Botnet" category.Anonymizersare services or tools that protect users' privacy by masking their IP addresses or routing their traffic through multiple servers. This category includes proxies, VPNs, and the Tor network, which anonymizes internet activity by routing traffic through a distributed network of relays. IPs and domains associated with these services are categorized under "Anonymizers" feeds.Exploitsare methods used to take advantage of vulnerabilities in systems, applications, or networks to gain unauthorized access or cause damage. These vulnerabilities can exist in software, hardware, or configurations, and exploits are designed to exploit these weaknesses to compromise security.Spamrefers to unsolicited and often irrelevant or inappropriate messages sent over the internet, typically in bulk, to promote products or services, or simply to flood inboxes. These messages can appear in various forms, including emails, comments, or social media posts, and are often used to distribute malicious content or scams. Many of the spam feeds we use are based on an older technology known as DNS-based Blackhole Lists (DNSBLs).
¶ IP Lookup

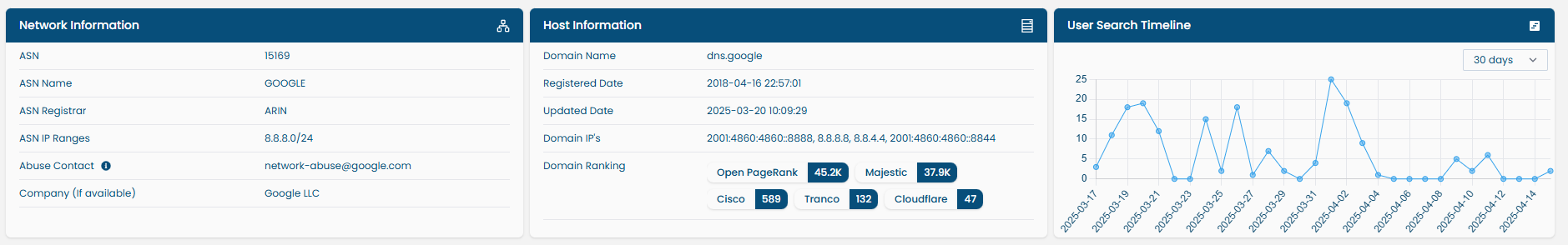
When performing an IP address lookup, the following information is displayed:
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Reputation Score | Aggregated from multiple threat feeds and scoring engines. |
| Vendor Feeds Check | Indicates whether the IP is listed in known blacklist or whitelist feeds. |
| Network Information | ASN, ISP, Country, Reverse DNS, etc. |
| Host Information | Device fingerprint, OS guess (if available), etc. |
| User Search Timeline | Graph showing search frequency of this IP by other users over the last 30, 60 or 90 days. |
| Google Search | Google search of the indicator |
¶ Bulk IP Lookup
Bulk IP Lookup: Users can search up to 20 IPs at once via input.
¶ How to Use:
- Paste up to 20 indicators into the search field.
- The system will:
- Detect IOC type automatically.
- Perform concurrent lookups.
- Display results in a tabular format with score summary.
¶ URL Lookup
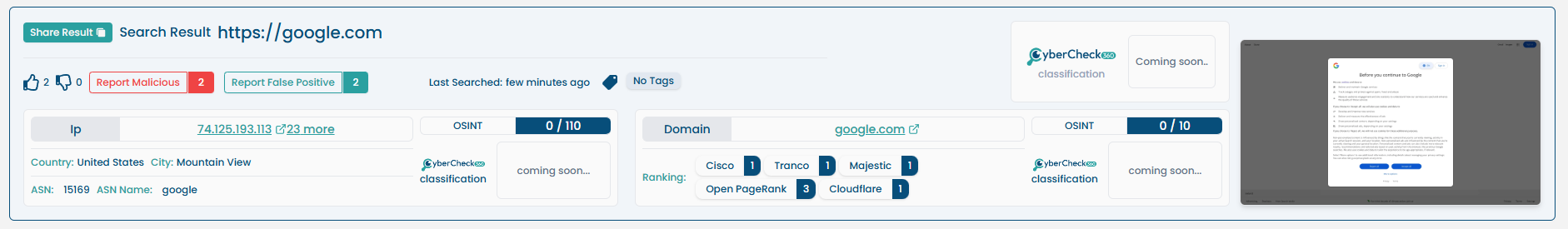
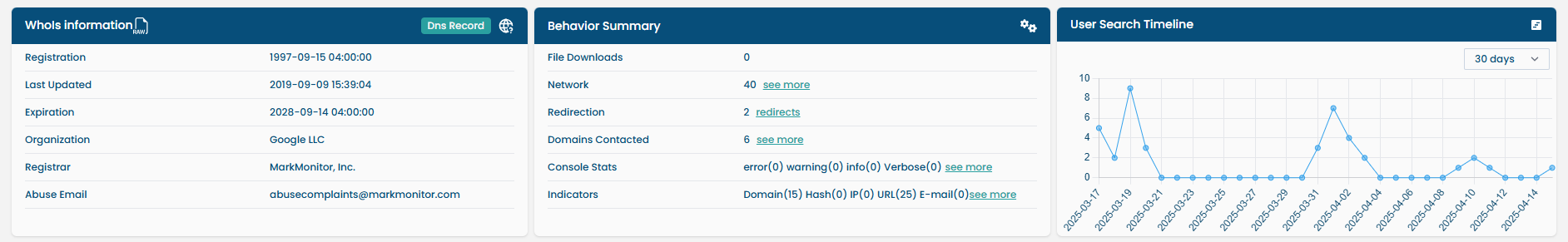
When performing a URL lookup, the following data replaces network/host info:
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Reputation Score | Threat score and flags based on scans and vendor feeds. |
| WHOIS Information | Domain registrant, registrar, and creation/expiry dates. |
| Behavioral Summary | Page content, scripts observed, redirection behavior. |
| Website Screenshot | Visual preview of the URL at the time of scan. |
| Resolved IP Info | IPs the URL resolves to, with reputation scores. |
| Domain Ranking | Alexa or similar global ranking. |
| Search Timeline | Activity timeline for the same URL by other users. |
| Google Search | Google search of the indicator |
URL's are automatically normalized and decoded before lookup.
In addition to the core URL analysis features such as reputation scoring, WHOIS, screenshot, and domain ranking, the platform provides two advanced tabs:
¶ Inspect Elements Tab
This tab emulates Developer Tools (DevTools) for analysts to do a deep behavioral dive into how the website operates in the browser.
¶ Sections Available:
-
Console Logs
View console messages, JavaScript errors, and runtime warnings triggered by scripts on the page. -
Network Requests
See real-time requests made by the webpage — including DNS queries, API calls, JavaScript imports, and beacon traffic. Useful for detecting:- Malicious redirects
- Beaconing activity
- C2 communications
-
Application Storage
Inspect cookies, local/session storage, and service workers. Useful to spot:- Tracking behavior
- Suspicious persistent cookies
- Token or credential leakage
All actions are sandboxed and safely rendered in a secured browser environment.
¶ Extracted Indicators Tab
The platform automatically extracts and classifies IOCs embedded or referenced in the URL’s webpage.
¶ IOC Types Detected:
- IP addresses
- Domains
- URLs
- Hashes (MD5, SHA1, SHA256)
- Email addresses
¶ Output Includes:
- IOC Type
- IOC Value
- Frequency (Number of times it appeared)
- Lookup Button – One-click to view full details of that extracted IOC
This helps uncover:
- Hidden threats embedded in the page (e.g., dropped links, C2 URLs)
- Redirect chains or embedded scripts leading to external IOCs
- Contextual clustering of related malicious infrastructure
¶ Example Use Case
- A suspicious shortened URL resolves to a redirect chain that leads to a phishing page.
- Console logs reveal obfuscated JavaScript used to load a credential-harvesting form.
- Network tab shows outgoing beacon to a known C2 server.
- Extracted indicators show additional domains/IPs referenced via iframe or image tags.
- Analyst can instantly lookup those IOCs to trace the infrastructure or report further.
These advanced tabs make URL inspection not just a scan — but a live browser intelligence session.
¶ Domain Lookup
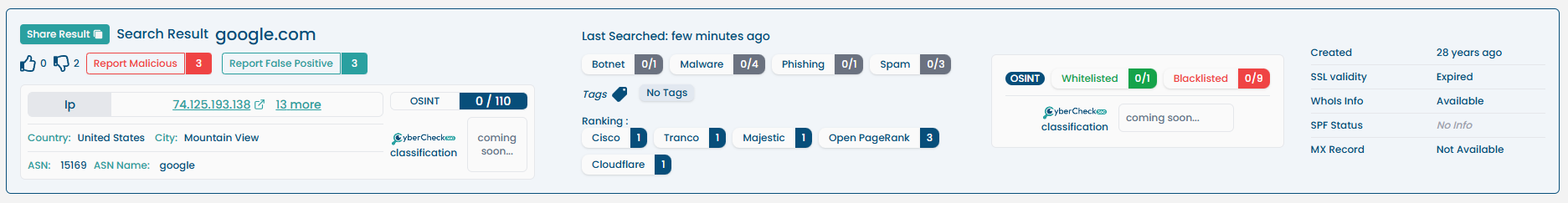
For domains, the following specialized information is included:
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Reputation Score | Aggregated threat reputation. |
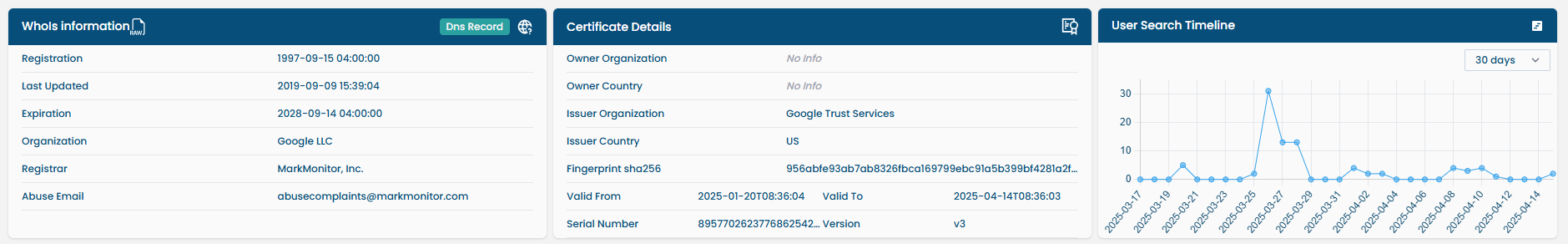
| WHOIS Information | Registrar, registrant details, domain age, etc. |
| SSL/TLS Certificates | Certificate chain, issuer, expiry date, and fingerprint. |
| Resolved IPs | Associated IPs and their reputation scores. |
| Domain Ranking | Global visibility score (e.g., Alexa, Majestic). |
| Search Timeline | 30-day frequency history of domain lookups by users. |
| Google Search | Google search of the indicator |
Domain aliases (e.g.,
wwwvsnon-www) are resolved and mapped internally.
Alongside the core features like WHOIS, certificate details, resolved IPs, and threat scoring, the Domain Lookup section includes a Subdomains Tab for deeper infrastructure mapping.
¶ Subdomains Tab
This tab lists all discovered subdomains associated with the queried root domain. It helps analysts understand the broader infrastructure and potentially malicious or forgotten subdomains still pointing to active servers.
¶ Key Features:
-
Subdomain Enumeration
Uses both passive and active DNS sources to identify subdomains. -
Output Includes:
- Subdomain name (e.g.,
mail.example.com) - Resolved IP address (if available)
- Subdomain name (e.g.,
¶ Use Cases:
- Discover attack surfaces (admin panels, APIs, staging environments)
- Identify hijacked or parked subdomains
- Investigate related domains in phishing or C2 campaigns
- Enable targeted blocking or monitoring on associated assets
¶ Subdomain Lookups
Every subdomain listed can be:
- Check for individual IOC lookup
- Cross-referenced with known malicious infrastructure
Example: A phishing site login-security.example.com is found under a legitimate domain. Lookup reveals it was resolving to a known C2 IP, and had an SSL cert issued just days ago.
The Subdomains Tab empowers analysts to go beyond surface-level lookups and build complete intelligence around a domain's digital footprint.
¶ Smart Scoring Engine
Reputation scores are calculated based on:
- Vendor feed weightage
- Past false positives
- Frequency of sighting in malicious contexts
- Time-decay (older indicators may have reduced score)
¶ Summary of Lookup Capabilities
| Feature | IP Lookup | URL Lookup | Domain Lookup |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vendor Feed Check | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Reputation Score | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| WHOIS Information | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Certificate Info | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Network/Host Info | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| Behavior Summary | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Screenshot | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Resolved IP Scoring | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Domain Ranking | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Search Timeline (30, 60 & 90 Days) | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Google Search | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Bulk Lookup (up to 20 IOCs) | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ❌ No |
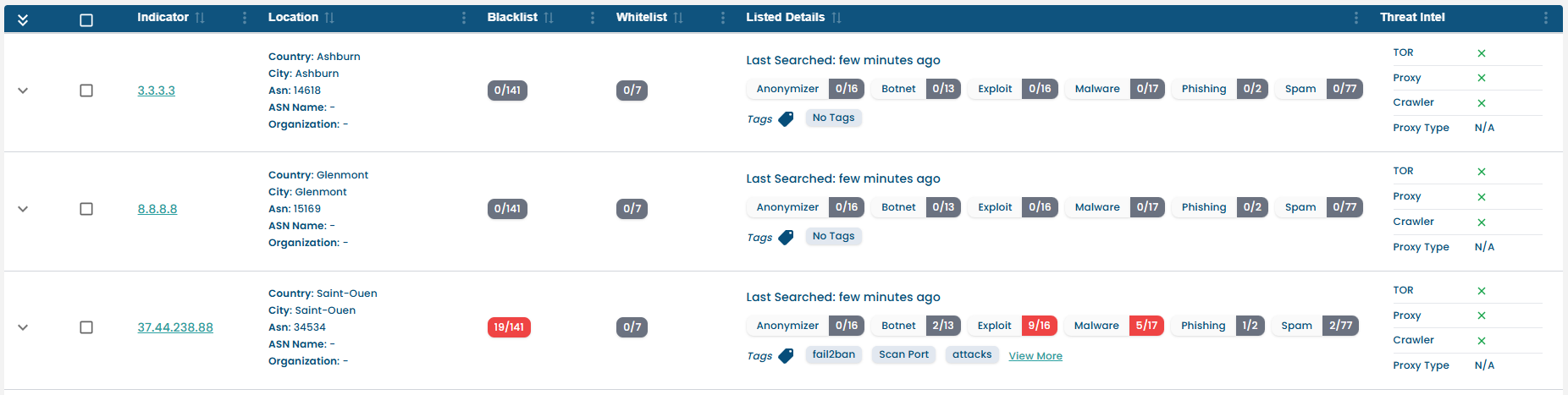
¶ Blacklist / Whitelist Feed Overview Tab
The Blacklist Tab allows users to view which threat intelligence feeds have marked a particular IOC (IP, Domain, or URL) as malicious (blacklisted) or safe (whitelisted).
This view helps analysts understand the broader community and vendor stance on a given IOC by categorizing it based on:
WhitelistSpamAnonymizerPhishingExploitBotnetMalware
¶ Feed Classification Example
Here’s how the threat intelligence feeds are organized in the interface:
| Category | Sample Feeds |
|---|---|
| Whitelist | SPFB, 0Spam, UCEProtect-Network |
| Spam | Blocklist.de, Stop Forum Spam |
| Anonymizer | Tor Project, Socks Proxy, Dan.me.uk |
| Phishing | Blocklist.de |
| Exploit | DShield, Turris, Bytefarm.ch |
| Botnet | Anti-Attacks, Abuse.ch, BotScout |
| Malware | FireHOL, Emerging Threats, CyberCrime |
¶ Each feed entry includes:
- Indicator Presence
- Expand option to show feeds (where available)
¶ IOC Types Supported
The Blacklist/Whitelist Tab supports:
- IP Address
- Domain
- URL
¶ Use Cases
- Quick Threat Attribution: Identify which vendors classify the IOC as malicious or safe.
- Confidence Scoring: More feeds listing an IOC as malicious increases confidence in its threat level.
- Cross-checking False Positives: Spot discrepancies across feeds to identify potential false positives or benign entities.
Example: An IP marked as malicious in Emerging Threats but listed as safe in SPFBL can indicate conflicting reports that need deeper investigation.
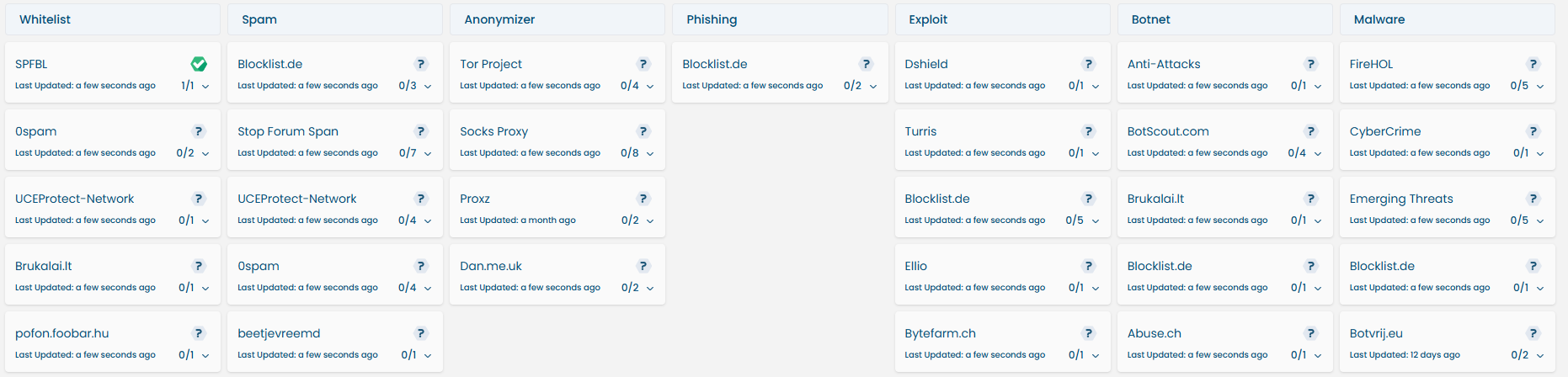
Visual snapshot of the Blacklist Tab showing feeds by category.
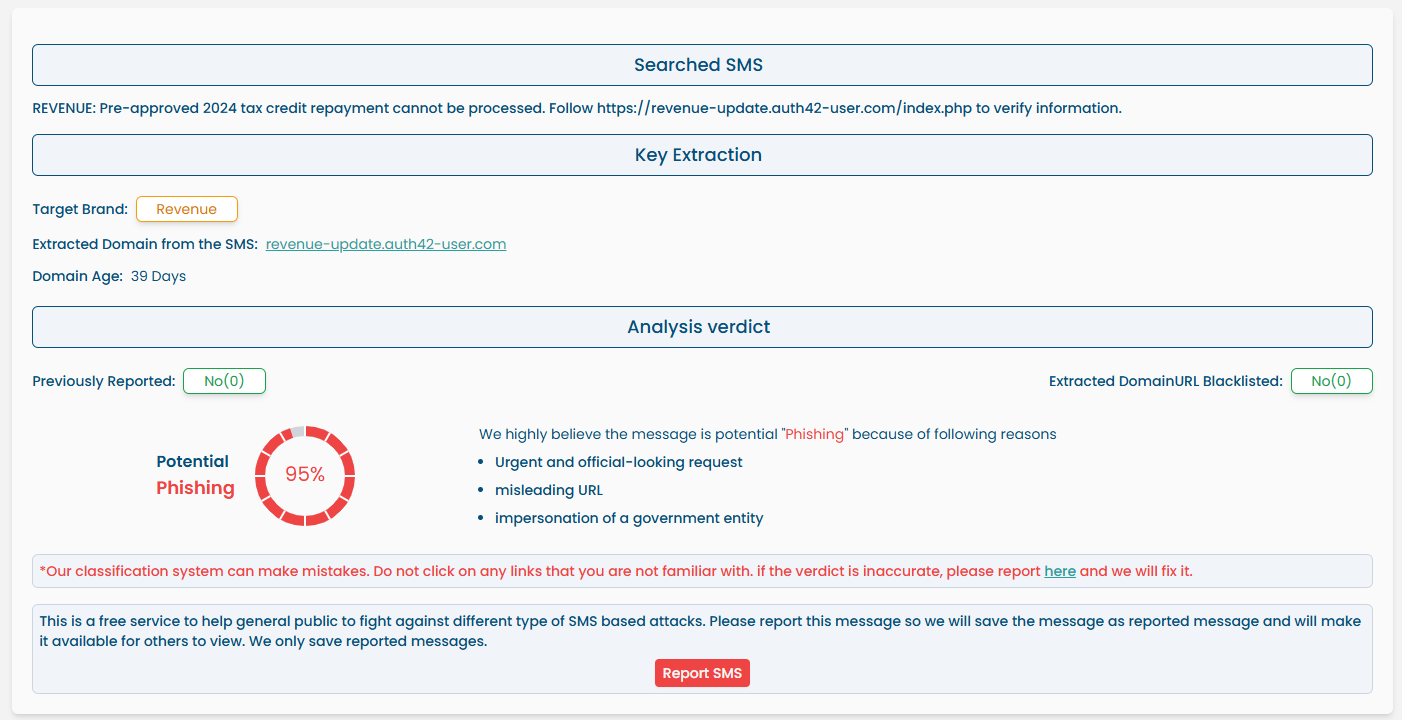
¶ SMS Verification
The SMS Verification section allows users to analyze suspicious text messages for potential phishing or scam content using AI-powered detection.
¶ How It Works
- The user pastes the SMS message into the input field.
- The system extracts any links or domains present in the message.
- An AI model analyzes the message content and link behavior.
- A detailed verdict is displayed including:
- Target brand (if any)
- Extracted domain or URL
- Domain age
- Blacklist status of the domain
- Phishing probability score (e.g., 95%)
- Reasons for classification (e.g., impersonation, urgency, misleading URL)
- Prior reports (if message has been reported earlier)
¶ AI-Powered Detection
We use trained AI model to assess:
- The language style and tone of the SMS
- The structure and domain patterns in embedded links
- Threat signatures based on previously reported phishing campaigns
Example Verdict:
Potential Phishing— 95% Confidence
“Urgent and official-looking request”, “Misleading URL”, “Impersonation of a government entity”
¶ Community Contribution
If the message is confirmed malicious:
- Users can click
Report SMSto submit it. - The message will be saved and made available to warn others.
- Reported data is also used to train and improve the model over time.
Only messages containing indicators (URLs/domains) will be verified. Plain text messages without any actionable content will not be analyzed.
¶ Safety Warning
Do not click on any links from suspicious messages.
The classifier may make occasional mistakes. If you believe the classification is wrong, you can report an error for reanalysis.
This tool is a free and privacy-respecting service to help the general public stay safe from SMS-based phishing attacks.
If you have suggestions for improvements or any misclassifications, please reach out. We're all ears!